
Wizz.com - Flash Report
Cement Manufacturing
The manufacturing of
Cement
is a large scale energy intense process that operates 24/7.
The process typically involves the operation of
Rotary Kilns
at high temperatures to achieve the Calcination (roasting or oxidization) of the raw feedstocks.
Cement is made primarily from a
Limestone
base (Calcium carbonate CaCO3) with a blend of alumina, silica, gypsum, other minerals, and iron.
Although, traditionally, the combustion of fossil fuels have been used as a source of heat for the kilns in the cement industry
(oil,
natural gas
&
coal)
there has been a shift towards the use of
Alternative Fuels.
Cement production is a significant generator of CO2 as an essential part of the oxidization process,
traditionally these
CO2 Emissions
have been released to the atmosphere.
Concrete Products
Cement is blended with Aggregates (sand and gravel) to form Concrete Products.
The cement component acts as a binder that hardens concrete into resilient shapes.
Concrete is one of the most commonly used building products used worldwide.
The recovery of end of life concrete structures makes
Concrete Recycling
one of the highest volume commodities reclaimed and reused.
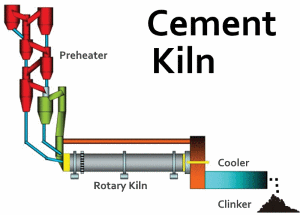
Fuel Requirements
A major cost in the production of cement is the fuel to operate the kiln.
In order to be economically competitive cement manufactures are constantly seeking
cheaper alternatives.
Traditional fossil fuels (oil,
natural gas
&
coal)
are shifting to the use of Alternative Fuels due to the
appetite for calorific values in both the preheating stage and in the primary kiln burner.
Solid Recovered Fuel SRF
Solid Recovered Fuel SRF, also known as Specified Recovered Fuel (SRF),
processes
waste
materials into specified sizing, calorific value and moisture content and may be pelletized or semi-densified.
RDF Refuse Derived Fuel,
ash or residues and residual minerals may be directly incorporated into the
Cement Clinker
Cement Clinker
Calcination (which is the process of heating a substance to a high temperature, but below its melting point,
in the absence of air, to bring about thermal decomposition) takes place within a rotary kiln.
This process produces an intermediary nodular material called clinker which is then further
blended and pulverized to produce a particular recipe or quality of cement.
A wide number of minerals may be included in the mix of raw kiln feedstock to produce cement clinker,
in addition, other minerals may be blended into the post kiln clinker.
These minerals may include a mix of both virgin or recycled materials that contain
lime,
calcium,
alumina,
silica,
gypsum
and other
materials
that are acceptable within the tolerance
for critical specifications for cement production.
In addition burner fuel ash or residues and residual minerals may be directly incorporated into the clinker.
The potential exists to consume Non~Metallic
Inorganic Content Composite Wastes.
Slag Cements
One common source of materials used as a feedstock in the manufacturing of cement is
Blast Furnace Slag (BFS)
generated as a by-product of the
Steel Making
process.
CO2 Emissions
A combination of high temperature
Combustion
and the kiln roasting process releases CO2 as a by-product from the reduction (oxidation) of limestone
in the production of
Cement Clinker.
In Traditional Cement Manufacturing it has been an acceptable practice to release the CO2 Emissions into the atmosphere.
In an effort to become carbon neutral the industry is moving towards a
closed loop emission capture and collection of the off gasses.
Some schemes propose the sequestration of the captured emissions,
other methods utilize the captured CO2 as a primary raw feedstock in a
Bio-Refining
process.
Thermal Waste Destruction
Some Cement Kilns are used for High Temperature Thermal Waste Destruction for the neutralization
of biological or pathological medical wastes as well as general and hazardous chemical wastes.
Cement Kilns may also be utilized as a waste treatment or disposal method for municipal solid waste
and commercial wastestreams that are sorted and processed into Solid Recovered Fuel
SRF
as a kiln combustion heat source.
Industrial Product & Commodity Trade
Cooksmill NetSystems operates an online
network
of exchanges that promote the trade of industrial products and commodities.
You may buy or sell any of the materials listed on this page by clicking on
the links and adding your trade inquiry.
The on-line exchange service directly connects Buyers and Sellers.
If we can assist you in any way in using the websites within the Cooksmill NetSystems
network,
please contact us at your convenience.
Please remember that you are responsible to perform your own due diligence on any prospective counter party
that you deal with and please
report
any abuse of our system.
Content on this page was produced for the benefit of
members
of the Cookmill NetSystem network.